Pressure Sensor
FAQ
About Sensor Installation
- What should be done to eliminate the influence of noise?
- First of all, install the sensor as far from the noise source as possible.
- If doing so does not work, connect the ground to the frame on which the sensor is installed.
- If the influence of noise is still suspected nonetheless, it is recommended to use a commercial noise filter.
- What should be done to prevent condensation?
- First, dehumidify the room with air-conditioner.
- If the sensor is directly installed on a cooling pipe, provide a connection pipe to set the sensor apart from the cooling pipe by more than 30 cm, so that the difference between the sensor temperature and ambient temperature may be within 5°C.
- Can you tell me the working temperature?
- Please confirm the compensated temperature range and safe temperature range shown in the product specifications on this site. The former shows the range where the accuracy of the product is guaranteed, and the latter is the range where the product can be used without failure.
- When using the sensor in low temperature, make sure the location where the sensor is used will not be frozen.
About Products
- What do "oil free processing" and "water free processing" mean?
- Oil-free processing refers to a treatment that has been cleaned to ensure that no oil remains or adheres to the pressurized parts.
- Water-free treatment refers to the cleaning process in which moisture does not adhere to or remain on the pressurized parts.
- However, it does not apply to the gaskets and drain cocks of the accessories.
- Is it possible to make sensors for the range other than those shown in the website?
- Yes, it is.
However, some restrictions on the accuracy or temperature characteristics may apply. Contact our Sales Department in advance.
- Yes, it is.
- Can chemical or gases that cause corrosion be measured?
- Basically, stainless steel materials such as SUS316L or SUS630 are used in the connecting parts of pressure ports of VALCOM sensors. Measurement is possible as long as your media to be measured do not corrode these materials.
- What is the difference between the gauge pressure (atmospheric pressure) and absolute pressure?
- Basically, gauge pressure (atmospheric pressure) is based on the pressure of the atmosphere where the sensor is placed as zero (reference), and absolute pressure is measured from absolute zero, the pressure in a vacuum (approx. 10 Pa or below).
- What should be done to protect against excessive pressure or pressure surge?
- If a pressure surge occurs, the peak value may be five times the normal pressure. In such a case, it is recommended to provide an orifice or other fitting to reduce the pulsation pressure.(Refer to the Options page.)
- What is water hammer phenomenon?
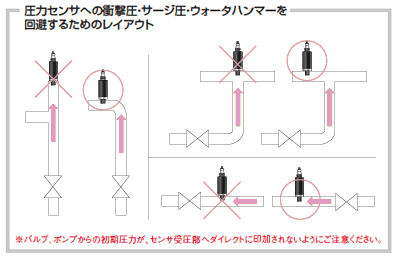 If flow rate is changed abruptly by using a valve, a severe and transient pressure fluctuation may occur, thus causing a hammering noise. This is called water hammer phenomenon. If water hammer occurs, excessive pressure will be exerted on the pressure port of the sensor, which may lead to failure.
If flow rate is changed abruptly by using a valve, a severe and transient pressure fluctuation may occur, thus causing a hammering noise. This is called water hammer phenomenon. If water hammer occurs, excessive pressure will be exerted on the pressure port of the sensor, which may lead to failure.
- Is it possible to extend the cable length?
- When connector (standard/waterproof) connection is selected, it is possible to connect an extension cable up to 200 m.
In this case, it is recommended to select current output [4 to 20 mA (2-wire)]. Note that, if voltage output is selected, the output voltage will drop due to the resistance of cable.(Current specification is recommended for long distance transmission.) - The same applies if the cable is to be extended by the customer.
In this case also, it is recommended to select current output [4 to 20 mA (2-wire)] if the cable is to be extended by more than 10 m. - Extending or shortening the cable for the separate sensor type will affect the accuracy. Contact our Sales Department if you plan to do so.
- When connector (standard/waterproof) connection is selected, it is possible to connect an extension cable up to 200 m.
Pressure Sensor
